If you’re interested in doing some cool things with your career, I suggest getting into data analytics. Just a year ago, we asked thousands of business leaders, IT professionals and hiring managers about the key technologies and skills that would grow revenue for their organizations through 2023. As you can see in Figure 1, 46% of the respondents gave a list of key growth drivers, from IoT to the cloud to data analytics.
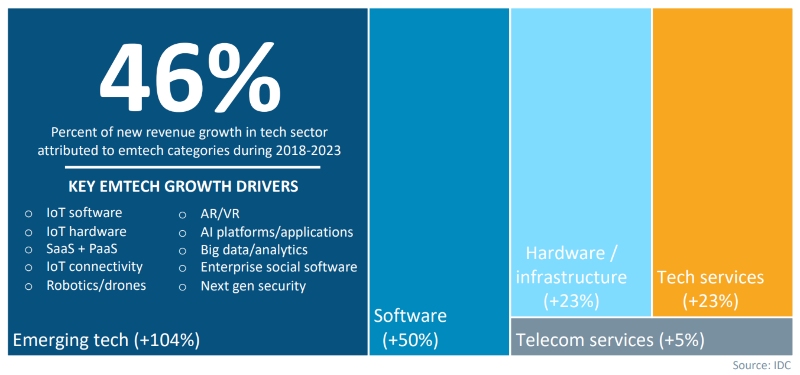
Figure 1: Key growth drivers through 2023
When it comes to my career, I’ve always tried to focus on long-term trends and needs. The results of this survey really opened my eyes to the importance of data analytics as a skill set for the future; after all, if “data is the new oil,” as the cliché goes, then it’s wise to know how to drill into data fields to generate new value for your organization.
I also noticed that this survey indicated that artificial intelligence (AI) and internet of things (IoT) were important. This is striking, because data analytics makes it possible to glean actionable information from the data generated by IoT devices. You see, data analytics makes it possible for organizations to derive revenue from IoT devices. That’s pretty interesting.
And that’s just our 2021 report. According to the CompTIA IT Industry Outlook 2022 report, we’re at the cusp of a data revolution. Key areas go beyond simple database administration – admittedly the most-known area – and into skills that include data management, visualization and predictive analytics, as shown in Figure 2.
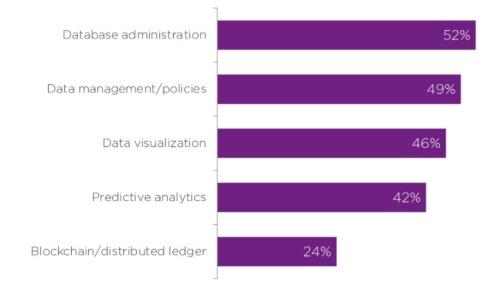
Figure 2: Key data skills, per the CompTIA 2022 Industry Outlook report
The same report indicates that today’s organizations are focused on reaching new customer segments, as shown in Figure 3.
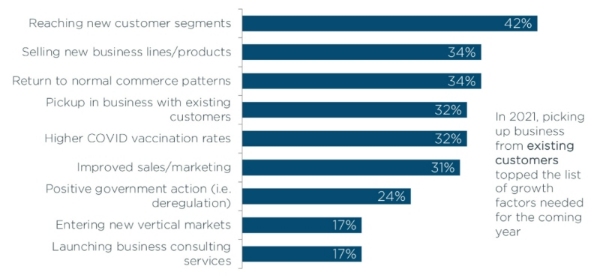
Figure 3: Key areas of focus for today’s businesses
The best way organizations can reach new customer segments and sell better is to follow the data.
Wait – Should I Get Into Data Analytics or Data Science?
I’m specifically talking about data analytics. There’s a difference between data science and data analytics, as you can see from Figure 4.
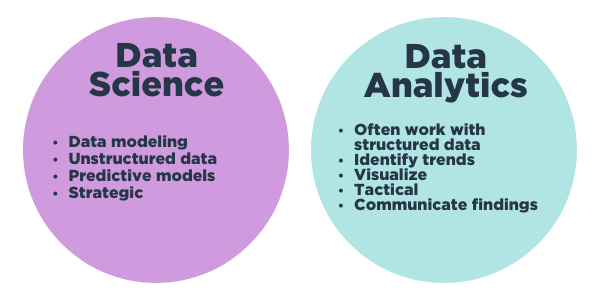
Figure 4: Data science vs. data analytics
A data scientist does predictive modeling and works with unstructured data – the data that doesn’t fit nicely into a spreadsheet or database. Unstructured data comes in myriad forms, including video files, audio and image files, log files and even data exhaust, which is the random data generated when users access the internet.
A data analyst generally focuses on structured data – the things you find in a spreadsheet. They help identify and visualize trends. When a company needs someone to sift through data and discover a trend, they turn to a data analyst.
A data analyst manipulates data to make sure it’s accurate. They help create confidence, because they make it possible for organizational leaders to understand what the data is telling them, through data visualization. You could argue that a data analyst would work for a data scientist, in many cases.
We need lots of data analysts, and though there is a learning curve, it’s not as steep as the journey to become a data scientist. After all, why not go into data analytics, succeed there, and then have your company pay for you to become a data scientist?
So, What Does a Data Analyst Do?
For one thing, you take fairly random data and mine it for trends. Using software including Microsoft Excel, data analysts apply various methods and techniques to tease out trends. They help business leaders, for example, review and refine the questions they have about data and help draw meaningful connections.
For example, I’ve been lucky enough to know a data analyst who helps companies create websites. Her name is Oluwaseyi (Seyi) Faleke, and she works for a company called Anthro-Tech. She and her co-workers spend time sifting through client lists, webpages, log files and web analytics reports. This type of data is called quantitative data because it is measurable and countable.
This type of data is critical, because it helps organizations understand the size and nature of an audience, or identify trends within data. She then works to discover meaningful trends within all of this data by eliminating extraneous information, which can include outliers, or pieces of data that may seem relevant, but are actually anomalous and less important than major trends.
In addition to working with quantitative data, she works with clients to create focus groups. She leads these groups to help gather additional data. This additional data is called qualitative data because it helps describe and make sense of the quantitative data. Analysts often use both types of data to create a more complete picture of a particular issue or business question.
Data Analytics Job Roles and Your Career Pathway
Data analytics skills are important to myriad job roles. Here are just a few that are relevant to the CompTIA Data+ certification:
- Business analyst: Retrieves structured data and organizes it in ways that helps organizations draw meaningful, accurate conclusions. This data is then used to help determine business strategy or craft customer experience (CX) campaigns.
- Human resources analyst: Many times, this data is used to help improve employee experience (EX), morale and ensure that the organization runs smoothly.
- Quality assurance worker: Uses data analytics to identify issues and opportunities in products that are created by a factory or business process.
- Data quality analyst: Applies statistical methods and techniques to ensure that data used to make decisions is accurate.
The Intersection of Data Analytics and IT
Most data analytics jobs are outside of typical IT pathways. Yet, there are major intersections between data analytics and IT. Many data analysts begin as IT workers, and then years later find themselves working with data all of the time.
Tim Niles, for example, is a data analyst who works for Cisco’s HR department. He started his career at the help desk after earning big 3 CompTIA certifications: A+, Network+ and Security+.
Now, he helps Cisco ensure that its culture helps employees thrive. He is an example of someone who moved from being a data janitor to becoming a data curator. Tim spends his time sifting through applications such as PowerBI, Microsoft Excel and other data sources to spot trends and help his company move forward with confidence concerning its policies and procedures.
I also know many IT pros and managers who spend quite a bit of time sifting through data. For example, help desk and technical support service managers need to analyze help desk tickets to identify issues and make their departments more efficient.
In short, learning about data analytics can help you transform from a help desk technician to a help desk analyst and manager or a security administrator to a threat hunter.
There are quite a few intersections between IT and data analytics skills, as shown in Figure 5.
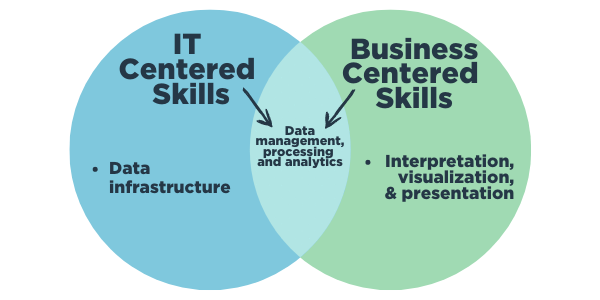
Figure 5: Intersecting IT, business, and data analytics skills
IT pros have skills related to data infrastructure, and data analysts have skills related to the interpretation, visualization and presentation of data. But the overlap comes in with data management, processing and analytics. These can be found in both disciplines.
How To Get the Data Skills You Need
Organizations worldwide need data-centric workers in order to thrive.
If you’re interested in learning more from working experts, check out the following resources:
- CompTIA Instructor Network (CIN) PULSE presentation, with Tim Niles and Oluwaseyi Faleke about Data+ and key data job roles.
- AFCEA CERTS conference: The Data Skills All Security Professionals Should Know (available on demand).
- CompTIA / IntellectualPoint webinar: Plan your CompTIA Career Path (Free registration, available on demand).
- The CompTIA IT Industry Outlook 2022
And check out the new CompTIA Data+ certification, available now. CompTIA launched a full suite of self-study training solutions as well as live online training to help you get the skills you need to get certified and grow in your career.
CompTIA Data+ covers the skills you need in data analytics. Start gaining skills like data visualization, data mining and more with CompTIA CertMaster Learn + Labs for Data+. Sign up for a free trial today!

